Low molecular weight proteins of barley related to food allergy
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.18832/kp2024.70.961Keywords:
barley, allergy, protein, beerAbstract
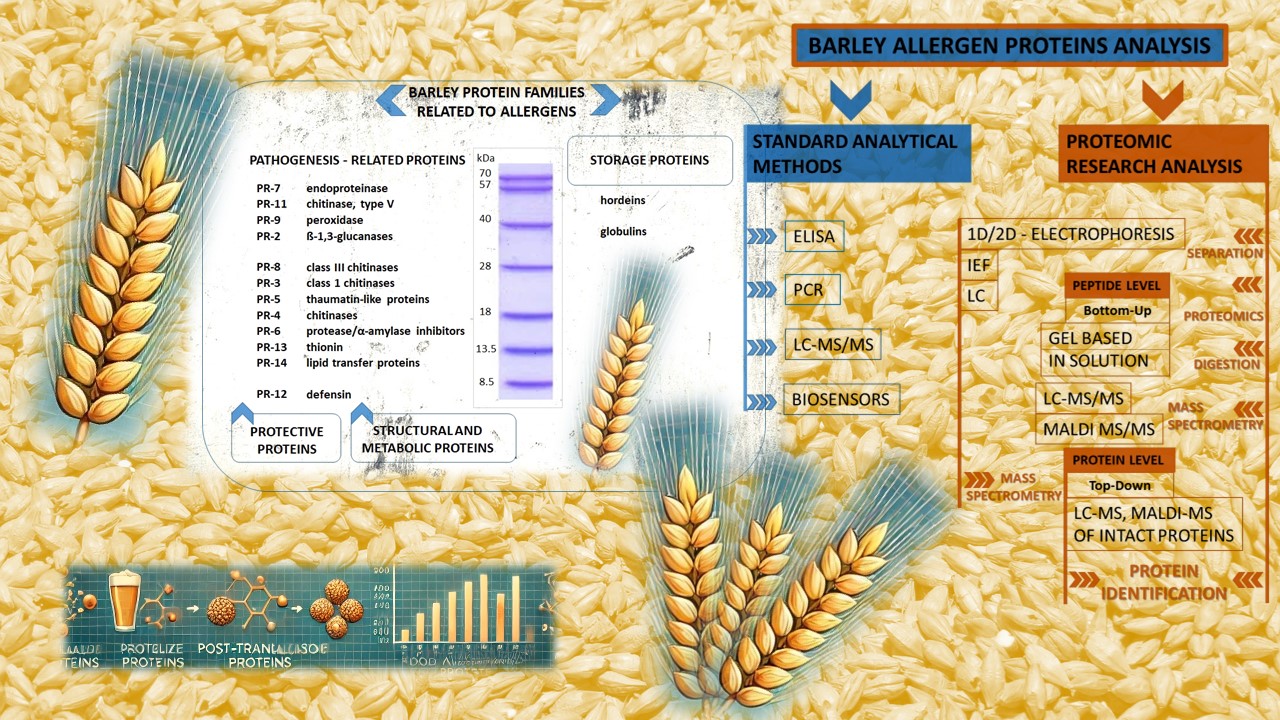
As protein composition and modification are critical for malt and beer quality, proteomic approaches have the potential to improve malting and brewing processes, as well as to monitor and characterize important low molecular weight proteins related to food allergy. New product compositions and industrial processes create additional needs that require much greater technological development. The detection and quantification of allergenic proteins by mass spectrometry is promising and contributes to greater accuracy, thereby significantly improving consumer information. In the case of allergenic proteins, a wide range of isoforms, post-translational modifications and other structural changes during the technological process can increase or decrease their allergenicity. In this context, we focused on tracking barley proteins related to pathogens, a large proportion of which are allergy-related. These mainly include a group of protease/amylase inhibitors such as α-amylase/trypsin inhibitor CMa, CMb, CMe, α-amylase inhibitor BDAI-1. Similarly, a lipid transfer protein 1 has been identified as a major beer allergen.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Janette Bobalova, Dana Strouhalova

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.







